


Next: Input Data
Up: The Crew Scheduling Problem
Previous: The Crew Scheduling Problem
Terminology
Among the following terms, some are of general use, while others
reflect specifics of the transportation service for the urban area
where the input data came from.
A depot is a location where crews may change buses and rest.
The act of driving a bus from one-depot to another depot, passing by
no intermediate depots,
is named a trip.
Associated with a trip we have its start time, its duration, its
initial depot, and its final depot.
The duration of a trip is statistically calculated from field collected data,
and depends on many factors, such as the day of the week and the start time
of the trip along the day.
A duty is a sequence of trips that are assigned to the same crew.
Any time interval between two consecutive trips in a duty is called an idle interval.
Whenever this idle interval exceeds Idle_Limit minutes, it is called a
long rest.
During a long rest, crews can leave the premises and return later to
resume their shift.
A duty that contains a long rest is called a split-shift duty.
The rest time of a duty is the sum of its idle intervals, not counting long rests.
The parameter Min_Rest gives the minimum amount of rest time,
in minutes, that
each crew is entitled to.
The sum of the durations of the trips in a duty is called its working time.
The sum of the working time and the rest time gives the
total working time of a duty.
The time, in minutes, that a crew member works in excess of
Workday minutes is called overtime and is given by
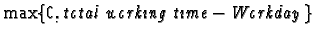 .
The Workday is a given parameter, specified by union
regulations, that bounds the maximum time
that an employee can work without incurring in overtime.
An upper bound on overtime is established by the parameter
Max_Overtime.
Finally, the maximum working time is given by
.
The Workday is a given parameter, specified by union
regulations, that bounds the maximum time
that an employee can work without incurring in overtime.
An upper bound on overtime is established by the parameter
Max_Overtime.
Finally, the maximum working time is given by
 .
.



Next: Input Data
Up: The Crew Scheduling Problem
Previous: The Crew Scheduling Problem
1999-12-16